February 7, 2018
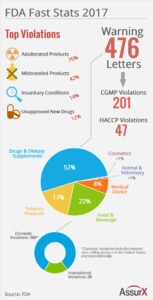
In 2017, the FDA released 476 warning letters. Top FDA warning letter violations were (1) adulterated products, (2) misbranded products, (3) insanitary conditions and (4) unapproved new drugs. Violations include drugs and biologics, food, medical devices, cosmetics, animal & veterinary products and tobacco products.
FDA Warning Letter: Manufacturer Type Breakdown
The breakdown of manufacturer type receiving FDA warning letters:
- 52% Drug Manufacturers
- 22% Food & Beverage Manufacturers
- 17% Tobacco Product Manufacturers
- 8% Medical Device Manufacturers
- <1% Animal & Veterinary Product Manufacturers
- <1% Cosmetics Manufacturers
A total of 388 domestic manufacturers received a FDA warning letter while 88 international manufacturers received a FDA warning letter. This correlates to approximately 82% of FDA warning letters issued to domestic manufacturers or companies with sales in the US. In addition, many warning letters target dietary supplements as well as tobacco products that are in violation of internet standards. This type of warning is global in nature as it affects all websites selling a product. Predictably, this trend will continue as observations are not always made at a physical point of manufacture.
FDA Warning Letters and cGMPs
Also of note were 201 deviations from Current Good Manufacturing Practice as advised in the Code of Federal Regulations Title 21 (CFR 21). Food and beverage manufacturers received 47 Hazard
Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) violations for food safety concerns.
Other FDA Warning Letter Trends Observed:
- Adulterated products failing to conform to compendial standards of quality, strength or purity were noted in 76% of all FDA warning letters.
- Expanding oversight continues from the Center of Tobacco Products. Vaping and tobacco product manufacturers and distributors received 80 warning letters in 2017 in accordance with Tobacco Control Act.
- Drug manufacturers, including finished pharmaceuticals, API and supplement manufacturers represent more than half of all cGMP violations (53%).
- Medical device FDA warning letters represented only 8% of total 2017 letters. Often, the drug under observation was part of a Combination Product but classified as a drug in the warning letter.
- Insanitary seafood preparation and packing still remains the most common HACCP violation (85%).
- Five individuals heading clinical trials were issued warning letters for out of protocol observations.
Conclusion
The FDA continues to focus investigatory efforts on the manufacture of drugs, both in the US and internationally. Food and beverage manufacturers still need to implement better methods for reducing insanitary conditions in their processing plants. An increase in oversight of tobacco products is expected to continue to increase. The FDA finds many responses to warning letters to be deficient due to lack of date in documentation and proof of corrective actions. The automation of quality management with an electronic QMS is the recommended solution. A traceable, end-to-end quality management system eliminates missing documents, provides alerts to issues at critical control points, streamlines complaint handling, and centralizes quality management processes for trending and corrective actions.

View the AssurX Webinar, 5 Pillars of a Modern Enterprise Quality Management System